08 Groundwater Modeling
08-07 Parameter Estimation & Calibration
Techniques for adjusting model parameters to match observations, including inverse methods and calibration strategies.
Contents
08-07-001Lumped Parameter Reservoir Model
| Type: Streamlit app | Time: 5–15 min |
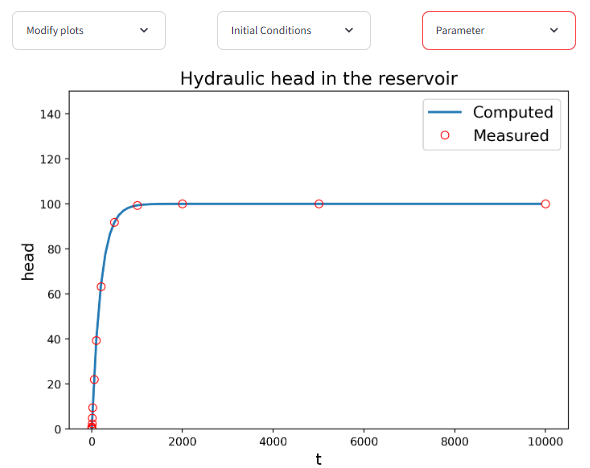
This interactive app introduces a lumped-parameter reservoir model as a simple conceptual representation of catchment or aquifer response. The system is described by effective parameters for recharge (R), storage (S), and conductance (K), linking inflow, outflow, and hydraulic head through a first-order mass-balance equation.
Users can interactively adjust model parameters and initial conditions to explore the temporal evolution of reservoir head and compare model results with predefined observation data. The app visualizes both the simulated head response and a measured–computed scatter plot, including standard goodness-of-fit metrics (ME, MAE, RMSE), enabling hands-on experience with basic model calibration.
The example is based on teaching materials by John Doherty and is specifically designed to illustrate parameter sensitivity, parameter correlation, and calibration challenges in conceptual models. It is well suited as an introductory exercise for students and professionals learning the fundamentals of model calibration and uncertainty in groundwater and hydrological modeling.
| Detail | Value |
|---|---|
| URL | lumpedmodel-reservoir.strea… · open app |
| Author(s) | Thomas Reimann (TU Dresden) |
| Keywords | model calibration, lumped model, non uniqueness |
| Fit For | self learning, online teaching, classroom teaching |
| Prerequisites | basic hydrology, basic hydrogeology, |
| References | Doherty, J. (2025) PEST, Model-Independent Parameter Estimation—Software and User Manual. Watermark Numerical Computing, https://pesthomepage.org/programs, last access 16. 12. 2025. |
Streamlit app details
| Detail | Value |
|---|---|
| Interactive plots | 2 interactive plot(s) |
08-07-002Analytical solution for 1D unconfined flow with two specified head boundaries - Understanding model calibration
| Type: Streamlit app | Time: 15–30 minutes |
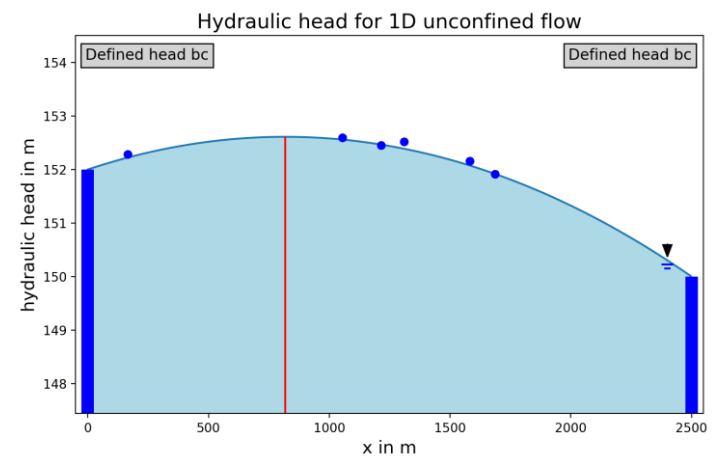
This app introduces the principles of model calibration using an analytical solution for one-dimensional unconfined groundwater flow with two specified head boundaries and uniform recharge. Starting from a simple conceptual and mathematical model, the app computes the hydraulic head profile and visualizes how the solution responds to changes in hydraulic conductivity and recharge.
To mimic real calibration workflows, the app can generate synthetic “measurement” datasets (regular or irregular sampling, optionally with noise). Users can fit the model by adjusting parameters and assess the quality of their calibration through a comparison of computed and measured heads, including an optional scatter plot and basic performance metrics (ME, MAE, RMSE). A feedback option reveals the “true” parameter values to support self-evaluation and learning.
| Detail | Value |
|---|---|
| URL | gwf-1d-unconf-calib.streaml… · open app |
| Author(s) | Thomas Reimann (TU Dresden) |
| Keywords | 1D flow, calibration, non-uniqueness, gamification |
| Fit For | self learning, classroom teaching, online teaching |
| Prerequisites | Darcy law, boundary conditions, groundwater flow equation |
Streamlit app details
| Detail | Value |
|---|---|
| Interactive plots | 2 interactive plot(s) |
Images
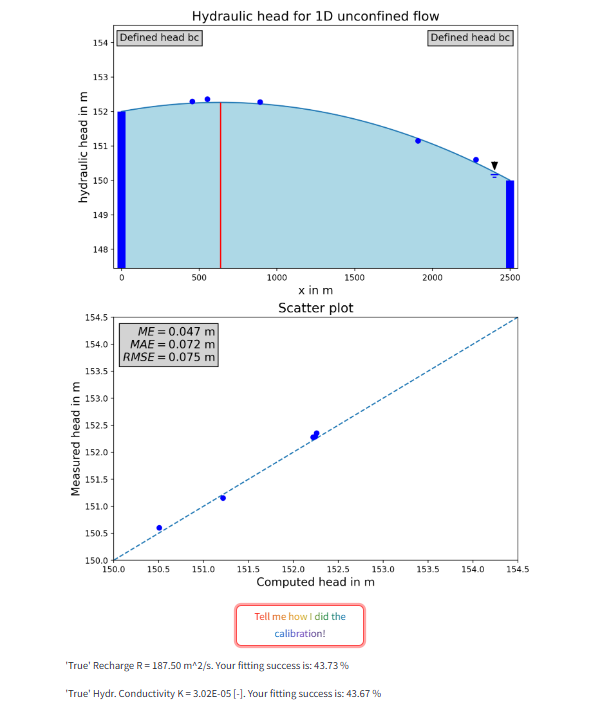
Figure 2: Interactive plots showing the model and the scatter plot. The solution provides learners a feedback about their calibration success. (Screenshot)
08-07-003Analytical solution for 1D unconfined flow with one no-flow boundary and one specified head/head-dependent boundary - Understanding model calibration
| Type: Streamlit app | Time: 15–30 minutes |
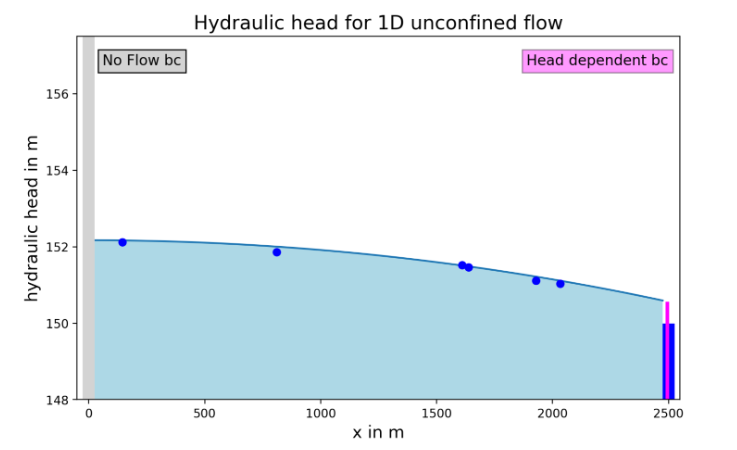
This app extends the 1D unconfined flow calibration exercise by introducing a no-flow boundary on one side and, on the other side, either a specified-head boundary or a head-dependent (river-type) boundary. The conceptual model assumes a homogeneous, isotropic aquifer with a horizontal impermeable base and uniform recharge over the entire model length.
Users can generate synthetic calibration datasets (regular or irregular sampling, optionally with noise) and then estimate model parameters by adjusting recharge and hydraulic conductivity. In the head-dependent scenario, an additional boundary parameter (river conductance) is included, allowing learners to experience how boundary formulation increases calibration complexity and parameter non-uniqueness. Model performance can be evaluated using an optional scatter plot and basic error metrics (ME, MAE, RMSE), and the app can reveal the “true” parameter values for self-assessment.
| Detail | Value |
|---|---|
| URL | gwf-1d-unconf-noflow-calib.… · open app |
| Author(s) | Thomas Reimann (TU Dresden) |
| Keywords | groundwater flow, 1D flow, unconfined flow, gamification, calibration, uncertainty |
| Fit For | self learning, classroom teaching, online teaching |
| Prerequisites | Darcy law, boundary conditions, groundwater flow equation |
Streamlit app details
| Detail | Value |
|---|---|
| Interactive plots | 2 interactive plot(s) |
Images
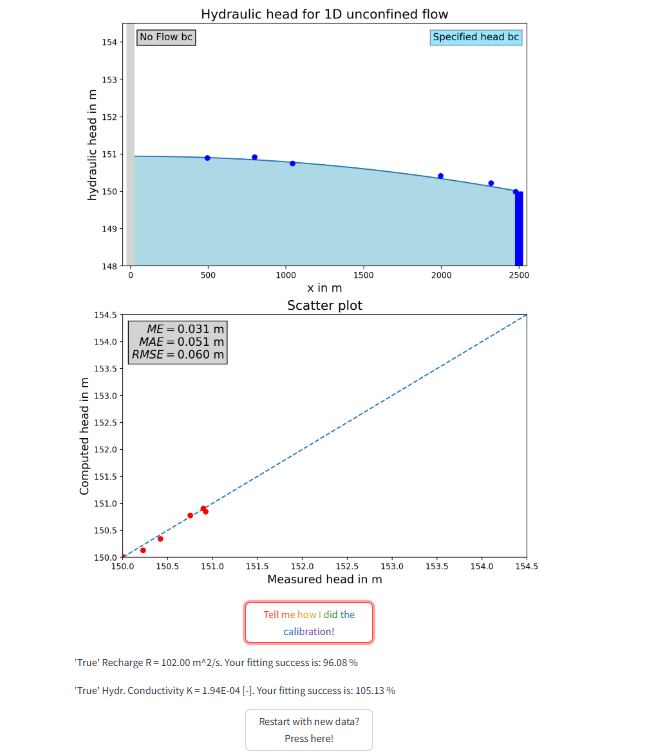
Figure 2: The user interface with the model, the scatter plot, and the results of the calibration. (Screenshot)