08 Groundwater Modeling
08-04 Transport Modeling
Advection–dispersion, numerical diffusion, Eulerian and Lagrangian approaches, numerical methods, particle tracking, MT3D and other software for solute transport simulation.
Contents
| Index | Description |
|---|---|
| 08-04-001 | Groundwater Particle Tracking |
| 08-04-002 | Groundwater Particle Tracking for multiple particles |
| 08-04-003 | Solute Transport Simulation with MT3DMS - 1D Transport in a Uniform Flow Field |
08-04-001Groundwater Particle Tracking
| Type: Streamlit app | Time: 5–15 min |
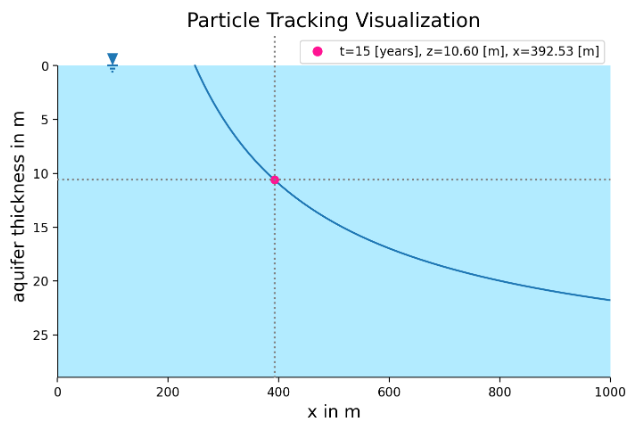
This interactive app illustrates groundwater particle tracking by following a conceptual tracer particle as it is transported through an aquifer by advective groundwater flow.
Users can adjust the entry position of the particle, the time since recharge, and key hydrogeological parameters such as recharge rate, aquifer thickness, and effective porosity. Based on these inputs, the app computes and visualizes the particle’s flow path and its evolving horizontal position and depth over time. A highlighted marker and guide lines show the particle location at a user-selected time step, helping to connect parameter changes directly to travel distance and travel time.
The module provides an intuitive introduction to a Lagrangian perspective on groundwater transport and supports discussion of travel times, flow paths, and the sensitivity of advective movement to recharge and aquifer properties under steady-state conditions.
| Detail | Value |
|---|---|
| URL | particle-tracking.streamlit… · open app |
| Author(s) | Edith Griesser (Universität Graz, Institut für Erdwissenschaften); Steffen BIrk (Universität Graz, Institut für Erdwissenschaften) |
| Keywords | particle tracking, lagrange, transport, solute transport |
| Fit For | classroom teaching, online teaching |
| Prerequisites | Basic hydrogeology, Aquifer parameters |
Streamlit app details
| Detail | Value |
|---|---|
| Interactive plots | 1 interactive plot(s) |
08-04-002Groundwater Particle Tracking for multiple particles
| Type: Streamlit app | Time: 5–15 min |
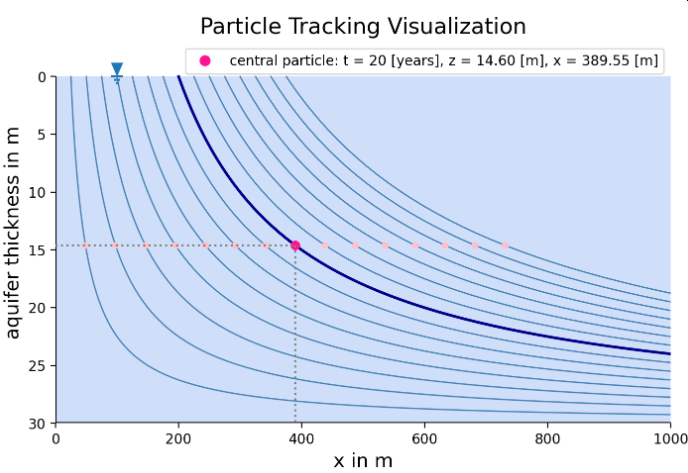
This interactive app extends the particle-tracking concept to a bundle of multiple groundwater particles, allowing users to explore how neighboring recharge points evolve into distinct yet related flow paths and travel times within an aquifer.
Starting from a central entry position, a user-defined number of particles is released with a specified horizontal spacing. All particles are advected by the same steady-state flow field, and their trajectories are visualized simultaneously. The central particle is highlighted, while the surrounding particles provide context on the spreading of flow paths caused by differences in initial position under identical hydraulic conditions.
By interactively adjusting recharge rate, aquifer thickness, effective porosity, entry location, and particle spacing, users can examine how small variations in starting position influence travel distance, depth evolution, and arrival times. The app supports discussion of advective transport, flow-path divergence, and travel-time distributions, and provides an intuitive introduction to multi-particle Lagrangian analysis commonly used in groundwater modeling and capture-zone assessments under steady-state conditions.
| Detail | Value |
|---|---|
| URL | particle-tracking-multi.str… · open app |
| Author(s) | Edith Griesser (Universität Graz, Institut für Erdwissenschaften); Steffen BIrk (Universität Graz, Institut für Erdwissenschaften); Thomas Reimann (TU Dresden, Institut für Grundwasserwirtschaft) |
| Keywords | particle tracking, lagrange, transport, solute transport |
| Fit For | classroom teaching, online teaching |
| Prerequisites | Basic hydrogeology, Aquifer parameters |
Streamlit app details
| Detail | Value |
|---|---|
| Interactive plots | 1 interactive plot(s) |
08-04-003Solute Transport Simulation with MT3DMS - 1D Transport in a Uniform Flow Field
| Type: Jupyter Notebook | Time: 15–30 minutes |
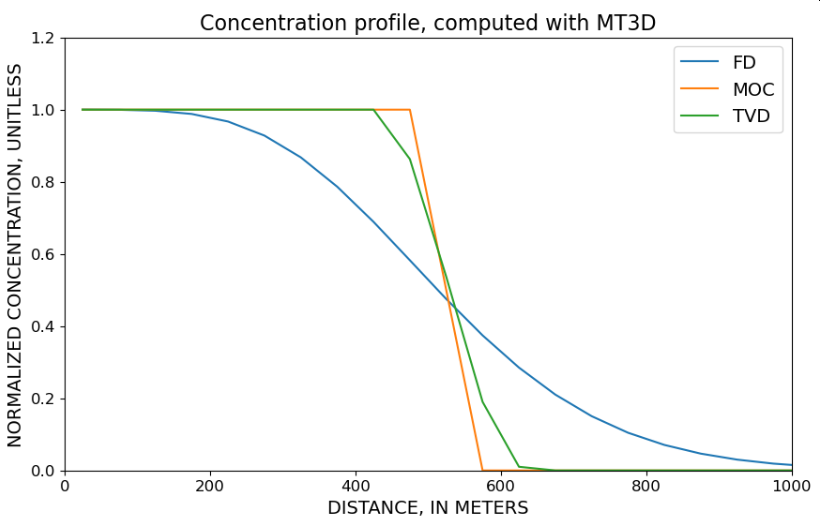
This application reproduces and extends the classical Example 1 from the MT3DMS documentation, illustrating one-dimensional solute transport in a uniform groundwater flow field. A coupled MODFLOW–MT3DMS model is used to simulate conservative and reactive transport processes under controlled conditions.
The app allows users to explore the influence of advection, dispersion, sorption, and decay on solute migration by systematically activating or deactivating individual processes. Different numerical advection schemes (finite difference, MOC, TVD) can be compared to assess numerical behavior, stability, and solution accuracy.
The model is implemented using FloPy for transparent pre- and post-processing, enabling users to focus on conceptual understanding rather than model setup. Concentration profiles, mass balance information, and method-dependent differences can be directly visualized and discussed. It is recommended to run the Jupyter Notebook on a local computer.
Intended use: Conceptual learning, numerical-method comparison, and advanced coursework in groundwater solute transport and numerical modeling.
| Detail | Value |
|---|---|
| URL | github.com · open repository |
| Author(s) | Thomas Reimann (TU Dresden) |
| Keywords | Groundwater modeling, solute transport modeling, heat transport modeling, MODFLOW, MT3D |
| Fit For | online teaching, classroom teaching |
| Prerequisites | Groundwater flow, solute transport |