05 Hydrogeochemistry and Contaminant Transport
05-06 Reactive Solute Transport
Coupling of chemical reactions with physical transport processes; conceptual and quantitative understanding of reaction fronts, plume evolution, and spatial–temporal geochemical changes.
Contents
05-06-001Mass balance for a decay chain - Decay of Species A to B and species B to C
| Type: Streamlit app | Time: 5–15 min |
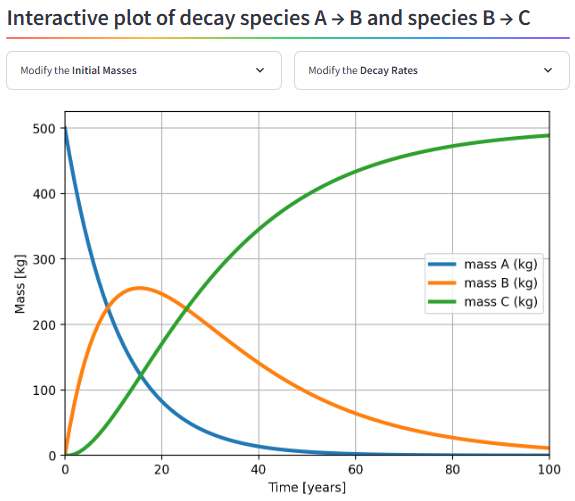
This interactive app illustrates the mass balance of a simple decay chain (A → B → C) using a time-discrete numerical approach. It demonstrates how the decay of one species leads to the production of subsequent species while conserving total mass.
Users can modify initial masses and decay rates and explore the temporal evolution of all three species through interactive plots. The example is motivated by radioactive decay but is formulated generically, making it applicable to a wide range of first-order transformation processes relevant to hydrogeochemistry and reactive solute transport.
The app is primarily intended as a conceptual teaching tool to support the understanding of coupled decay and production processes, mass conservation, and dynamic system behavior in environmental and groundwater-related contexts.
| Detail | Value |
|---|---|
| URL | radioactive-decay.streamlit… · open app |
| Author(s) | Thomas Reimann (TU Dresden, Institute for Groundwater Management); Rudolf Liedl (TU Dresden, Institute for Groundwater Management) |
| Keywords | solute transport, decay, half-time, reactive transport, mass balance |
| Fit For | self learning, classroom teaching, online teaching |
| Prerequisites | basic chemistry |
Streamlit app details
| Detail | Value |
|---|---|
| Interactive plots | 1 interactive plot(s) |
05-06-002Analytical solution for 2D instantaneous solute transport injection in porous media (with decay)
| Type: Jupyter Notebook | Time: 30–45 minutes |
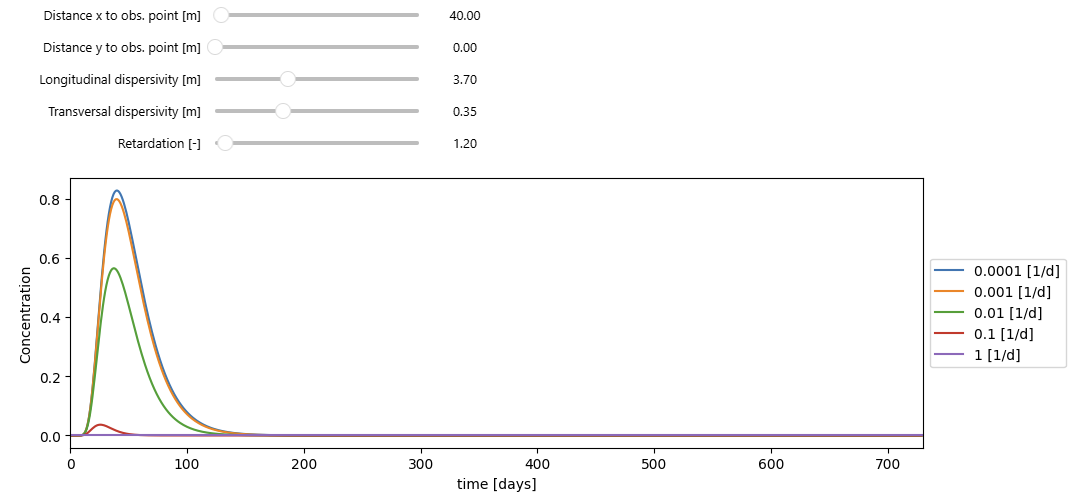
This interactive Jupyter tool computes and visualizes the analytical 2-D instantaneous solute injection solution with first-order decay in porous media. It simulates how concentration evolves over time at a given observation point for five contaminants, each defined by a different decay rate. The model incorporates:
- 1) Retardation
- 2) Longitudinal and transversal dispersion
- 3) Decay
- 4) 2-D spreading of an instantaneous point source
The user can interactively modify:
- 1) Distance to the observation point (x, y)
- 2) Longitudinal and transversal dispersivities
- 3) Retardation factor
The tool then automatically recalculates:
- 1) Effective velocity
- 2) Effective longitudinal and transverse dispersion
- 3) Time-dependent concentration curves
and plots the concentration–time profiles for all decay rates, allowing easy comparison of attenuation behavior in 2-D groundwater flow.
| Detail | Value |
|---|---|
| URL | github.com · open repository |
| Author(s) | Oriol Bertran (UPC); Daniel Fernàndez-Garcia (UPC) |
| Keywords | analytical solutions, solute transport, instantaneous injection, 2D, decay |
| Fit For | self learning, online teaching, classroom teaching |
| Prerequisites | None specified. |
| References | Bear, J. (2012). Hydraulics of groundwater. Courier Corporation. |